Kaspa is a blockchain platform that uses a unique and completely new technology, the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which allows multiple blocks to exist in parallel.
In short, it solves the common blockchain problem of high “orphan rate” (when, for example, two blocks are mined at the same time, but the network only accepts one).
Unlike traditional blockchains, Kaspa uses the GHOSTDAG protocol, which allows blocks created in parallel to exist side by side and be sorted by consensus. This approach, known as Block DAG, ensures secure operation while maintaining a high block creation rate.
Kaspa is the fastest and most scalable instant confirmation transaction layer ever built on the Proof-of-Work system. Transactions sent to miners can be immediately added to the ledger, which is built as a revolutionary new Block DAG technology.
The Ghost DAG/PHANTOM protocol is a scalable generalization of the Nakamoto consensus (Bitcoin consensus). Its design is faithful to the principles embedded in Bitcoin by Satoshi, Proof-of-Work mining. It is fully decentralized, which is maximally contributed by the absence of a circle of owners and the wide distribution of the amount of coins among users.
Kaspa (KAS) shows an extremely positive and upward trend in 2023 and 2024. Compared to other crypto assets, it was able to produce an upward trend even when the price of almost all other crypto assets fell sharply to the bottom in the bear market.
Solving the crypto trilemma
Traditional cryptocurrencies suffer from a security, scalability, and decentralization tradeoff: decentralized cryptocurrencies must limit the rate of block creation to limit the number of “orphans,” off-chain blocks that are created during the time it takes for latent blocks to propagate through the network. A high “orphan” rate reduces the efficiency of a PoW network, thereby reducing its protection against a malicious actor joining the open network. The Proof-of-Work consensus protocol generalizes Nakamoto’s chain into a directed acyclic block graph (Block DAG). Ghost DAG incorporates “orphan” blocks into the chain to create a Block DAG, then uses a novel MOHO algorithm to arrange the blocks in a way that favors well-connected, healthy blocks, quickly and with high probability. Ghost DAG allows Kaspa to bypass the traditional compromise of blockchains, improving block creation speed by orders of magnitude while maintaining Bitcoin's theoretical security guarantees.
This results in a cryptocurrency backed by 51% security, a large number of miners/nodes, and a throughput rate of 10 blocks per second. This is different from existing cryptocurrencies, which inevitably compromise with a small number of validating nodes or lower BFT security (a 33% threshold is required for malicious actors to attack the network).
(BFT = Byzantine Fault Tolerance) In peer-to-peer computing networks, Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) protocols are a popular solution for ensuring consistency security in the presence of some malicious nodes, and are therefore widely used in blockchain systems.
Kaspa, due to its unique and special features, will eventually find global adoption as the fastest, most secure, scalable peer-to-peer payment method with incredibly low fees. There is simply no other network or crypto asset that can compete with it.
Quick confirmations
The slow block creation rate of traditional cryptocurrencies results in slow confirmations, the time it takes for a transaction to appear on the blockchain. Kaspa’s consensus layer supports fast, sub-second confirmations – a fast first confirmation that enables use cases that require immediate confirmation of publication (but not immediate irreversibility), such as e-commerce.
High throughput
The slow block creation rate of traditional cryptocurrencies also results in low transaction speeds. Using Ghost DAG, Kaspa’s consensus layer changes the security protocol as a bottleneck for high throughput, allowing the block creation rate and block size to increase to a level that the network can handle. Kaspa also optimizes bandwidth costs and network infrastructure for high throughput.
Block creation speed

Kaspa is unique in its ability to support high block creation rates while maintaining the level of security offered by the most secure Proof-of-Work environment. Kaspa's current main net operates at a rate of 10 blocks per second.
Currently operating at a speed of 10 blocks per second, Kaspa aims to reach even higher speeds of 30 or even 100 blocks per second. This scalability and features set Kaspa apart from many other blockchain networks.
Special features include reachability, which allows users to query the DAG topology, block data pruning (with future plans for block header pruning), and SPV (Simple Payment Verification) certificates, a cryptographic technique that allows users to verify the validity of transactions without having to download the entire Kaspa blockchain.
The programming system was switched from the GOLANG programming language originally used to achieve higher speeds to the RUST programming language. After 100% node migration, it was possible to create 10 blocks per second, making it the fastest blockchain in the world. Before the transition, the new, faster system was tested on the test network for nearly a year to ensure a safe switch.
Network upgrade - Crescendo Hard Fork (10bps)

The crescendo hard fork was the switch from 1 bps to 10 bps, which was implemented without any problems on 2025.05.05. The developers main goal remains to significantly increase the number of blocks per second, which will attract the development of smart contracts and DeFi. In the future, the next step is 30 blocks and the ultimate goal is 100 blocks. This is currently not feasible, but later, as global adoption increases, it will be necessary for the network to be able to handle even hundreds of millions of transactions without problems and slowdowns. The project also boasts subnetwork support, which allows for the implementation of layer 2 solutions, paving the way for increased functionality and scalability.
Kaspa emission
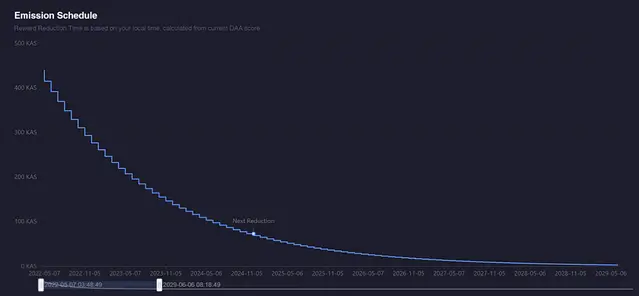
Another notable feature of Kaspa is its unique monetary policy. The project implements a geometric emission reduction over time, inspired by the 12-tone musical scale.
This policy, known as chromatic phasing, reduces block rewards in a way that aligns with the frequency of successive semitones on the tempered chromatic scale.
The initial block reward is set to the frequency of a Note A4, and the reward is halved approximately annually, with the amount of new Kaspa being released to the network decreasing by 5% approximately every 4 weeks. Since nearly 90% of the predetermined maximum supply of 28.7 billion Kaspa has already been issued, further issuance will not have a price-depressing effect going forward.
Mining decentralization
The slow block creation rate of traditional cryptocurrencies also causes large variations in mining revenue (i.e., irregular mining rewards due to the difficulty of finding a block) and encourages miners to join increasingly large mining pools that combine computing power and distribute smaller, more regular mining revenue to participants as the network grows, and block difficulty increases. This centralizes consensus power in the hands of a few pool operators. The fast block rate of Kaspa’s consensus layer reduces the dispersion of mining revenue, which reduces the incentive to join mining pools, contributing to mining decentralization.
Roadmap for significant developments related to the Kaspa network
Currently, the KRC20 network is the Kaspa Layer 2 network. Many new tokens are appearing on it every day (mainly meme coins for now), but of course any token category can be created on it. Its planned launch was June 30, 2024, but since it is a completely new development, there were minor errors in the beta version that was launched, so the new launch was postponed to September 15, by which time the Kasplex development team had fixed the errors. Since then, it has been working without problems, of course, this is still just a beta version and is being continuously developed.
The KRC721 network, which is required for NFT transactions, has been launched already.
Soon, USDT and USDC coins will be able to be attached to the Kaspa network via smart contracts. From then on, decentralized exchange will also be much easier and more widely available.
The launch of smart contracts is planned for summer 2025. From then on, it will have all the features of well-known large networks (e.g. Ethereum or Solana), but it will be much more usable due to the features detailed above.
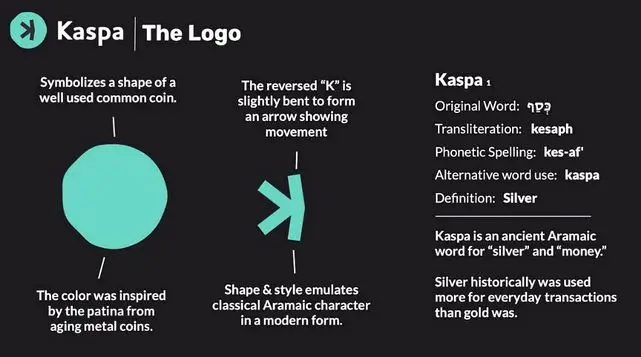
The origin of the name Kaspa
Useful links